| Home |
| Misc |
| Linux |
| TCP/IP |
| Windows |
| Random Daodejing |
| Photos |
Miscellaneous Things
Animal-Vehicle Collision Prevention w/ GIS / Virtual Reality Presentation Slides / Metropolis Ghost Town Documentary / Laboratory Information Management System / Buckminster Fuller Web Site / Record Database

(http://www.engin.umich.edu/caen/campcaen/photos/cave_princecar.jpg)
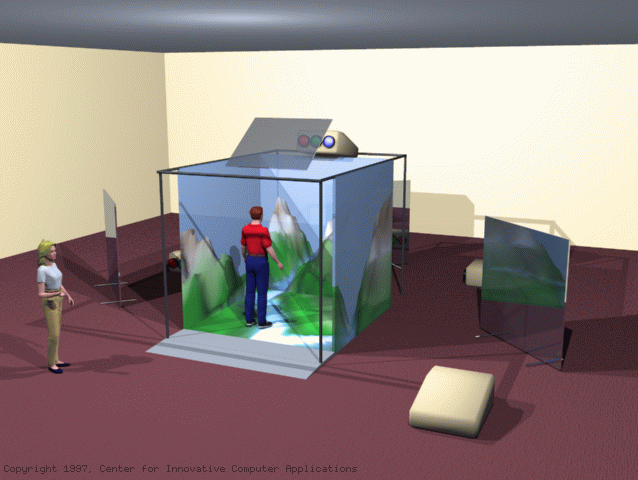
Virtual Reality?
- Simulate an artificial environment.
- Augment the existing reality.
- Accomplish some combination of the two.
Who Uses It?
- Medical
- Education
- Scientific research
- Architecture
- Entertainment
- Psychology
- Urban planning
- Resource extraction
- Archaeology
- Design

(https://inkido.indiana.edu/a100/handouts/Image116.gif)
Example - Medical
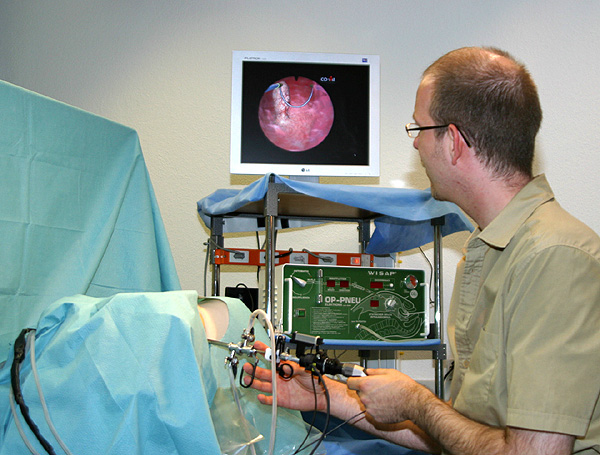
(https://co-me.ch/projects/phase2/p04/img04_00_01.jpg)
Simulation of medical procedures has allowed surgeons valuable practice and training experience.
Example – Architecture/Engineering
Architects, engineers, & urban planners can use virtual reality to examine 3D blueprints, prototype designs, and sometimes "walk through" virtual buildings and structures before they are built in real life.

(https://blog.digitalcontentproducer.com/briefingroom/
wp-content/uploads/2008/08/2-3d_interface_2d_preview.JPG)
(https://www.vr.ucl.ac.uk/projects/arthur/arthur2.jpg)
Example – Networked Communications & Virtual Worlds
Teleimmersion & virtual worlds, as well as personal “avatars,” have become commonplace as new forms of communication and expression.
(https://nanobugle.files.wordpress.com/2008/12/second_life-nanobugle.jpg)
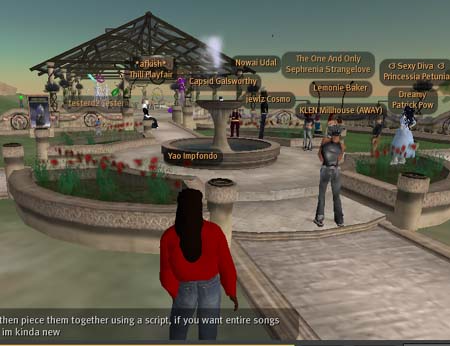
(https://www.ethanzuckerman.com/blog/wp-content/secondlife.jpg)
The Technology
- Motion tracking
- Haptic (tactile) technology
- Stereoscopy
- Omnidirectional treadmills
- etc.
The Philosophy
- Simulation
- Interaction
- Artificiality
- Immersion
- Telepresence
- Full-body immersion
- Network communication

(https://logicalscience.files.wordpress.com/2009/09/virtual-reality-8.jpg)
Contemporary Technical Apparatuses
Example of Head Mounted Display (HMD)

(https://www.jvrb.org/articles/34/figure2.jpg)
Early History
Modern History
Currently
Print Sources
Heim, Michael. The Metaphysics of Virtual Reality. Oxford: University Press, 1993.Rheingold, Howard. Virtual Reality: The Revolutionary Technology of Computer-Generated Artificial Worlds—and How it Promises to Transform Society. New York: Touchstone, 1991.
Sirius, R.U. True Mutations: Interviews on the Edge of Science, Technology, and Consciousness. Oakland: Pollinator, 2006.